Table of Contents
7 Tests for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Glaucoma Diagnosis is not only about Raised IOP, but we also need to assess the anterior chamber angle, Corneal Thickness, Optic nerve, visual filed.
- Due to multiple investigations required to diagnosis Glaucoma, most Eye hospital offer “Glaucoma Workup Package”.
- Following Tests need to be done to diagnosis Glaucoma:
- Slit Lamp Evaluation.
- IOP Measurement.
- Cup-Disc ration Analysis.
- Central Corneal Thickness.
- Visual Field Analysis.
- RNFL analysis.
- Gonioscopy.
1. Slit Lamp Evaluation for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- In slit lamp Examination we assess if there are any causative signs:
Pupil size and reaction:
- Raised IOP can dilate pupil and react slowly.
- Different pupil size between eyes also suggests raised IOP.
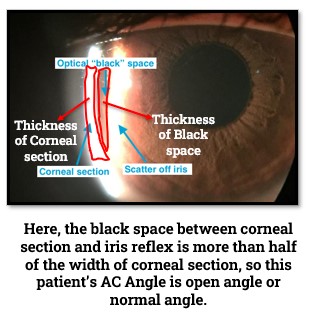
Von Herrick Technique for AC Angle:
- It’s qualitative procedure of assessment of AC angle.
- It’s done with optic section illumination with full length and narrow width and angle between illumination & observation system is 60° focusing on peripheral cornea.
- The gap (Black Space) between corneal section & reflected light on iris is compared with the width corneal section.
- If the width of Black space is half or more than the corneal section width, then the angle is considered Wide or normal.
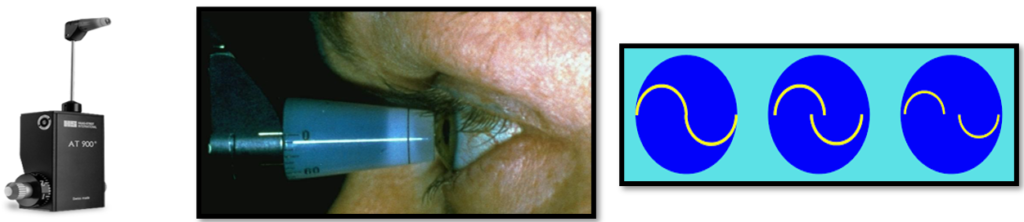
2. IOP Measurement for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Raised IOP is most common sign of glaucoma, but all the Tonometers are not equally accurate.
- Among all the Tonometers, Goldmann Applanation Tonometer is most accurate and considered as “Gold Standard” for IOP measurement.
- IOP more than 22 mm of Hg is considered Glaucoma Suspect.
- Most Tonometers are calibrated for a cornea with thickness 545 microns, so if corneal thickness varies more than 10 microns (560 or 540 microns), we need to correct the tonometer reading to get actual IOP.
We will discuss details about this in “Central Corneal Thickness Part.”
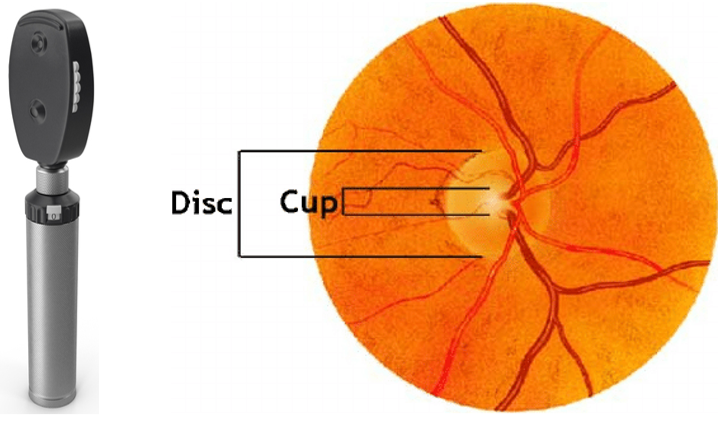
3. Cup: Disc Assessment for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Normal Cup: Disc ratio is 0.3 : 1.0, Cup : Disc ratio more than 0.4 : 1.0 is considered glaucoma suspect.
- Cup : Disc ration can be identified by either:
- Direct Ophthalmoscope.
- Fundus Photography.
- There is no specific scale to measure and compare the ratio between Cup & Disc.
- Clinician compare the ratio based on his own point of view, so this may vary from clinician to clinician
4. Central Corneal Thickness for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Almost all the Tonometers are built based on central corneal thickness is 545 microns.
- If Central Corneal Thickness is more or less than 545 microns, then we need to correct the IOP found in tonometry according to patient’s central corneal thickness.
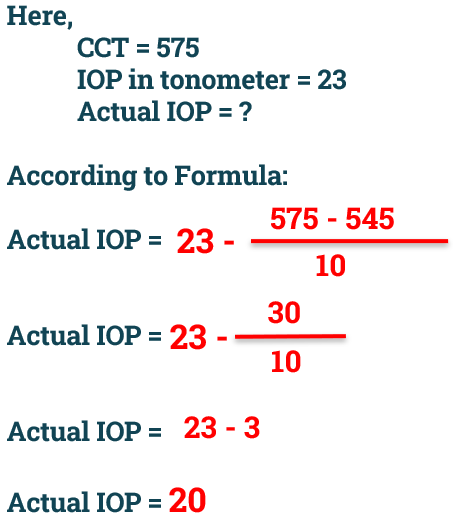
- Generally, for every 10 microns increased CCT, we need subtract 1 mm of Hg and for 10 microns of decreased CCT, we need to add 1 mm of Hg.
- Below formula can be used to get actual IOP of individual:

- Example: A patient IOP found in Non-Contact Tonometer (NCT) is 23 mm of Hg, patient’s Central Corneal Thickness is 575 microns. What is patient’s actual IOP?
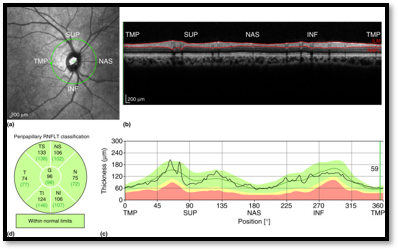
5. RNFL assessment for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- The weakest point of eyeball is Optic disc area due to passing Blood Vessel, Nerve, Retinal fibre etc
- When IOP raised, Optic disc area feels more pressure than other area.
- Due to constant pressure, Retinal nerve fibre keep dying & visual field defects develop.
- When Retinal Nerve Fibre layer get damaged, the thickness of Retinal nerve fibre layer gets reduced.
- In OCT, we can assess RNFL layer thickness changes for confirmatory glaucoma diagnosis.
- The retinal nerve fibres are arranged in way that when IOP raised it first affect Inferior area then Superior, Nasal & Temporal, respectively (ISNT).
- RNFL thickness of a normal eye (without glaucoma) is 80 microns or greater.
- If the average RNFL thickness is below 80 microns, then it’s considered glaucoma suspect.
6. Gonioscopy for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Most of the aqueous humour drains through anterior chamber angle, narrow or closed angle can lead to glaucoma.
- Gonioscopy helps to evaluate anterior chamber angle whether it’s wide open, normally open, moderately narrow, very narrow or closed.
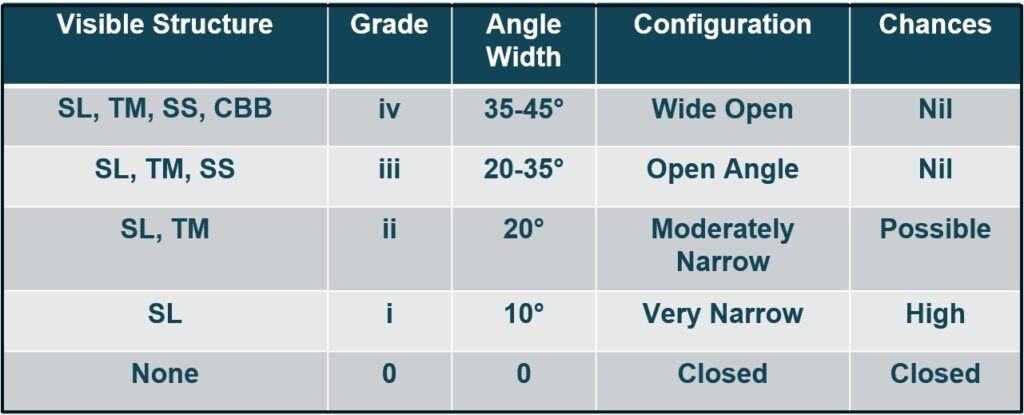
- Anterior Chamber Angle is formed by following structures:
- Root of Iris (RI).
- Ciliary Body Band (CBB).
- Scleral Spur (SS).
- Trabecular Meshwork (TM).
- Schwalbe’s line (SL).
- Depending Upon how many above structures are visible through the gonioscopy lens, Anterior Chamber Angle can be graded in 5 categories which is called Shaffer’s System.
7. Visual Field Analysis for Glaucoma Diagnosis:
- Visual field defects in glaucoma are initially observed in 10- 25 degree from fixation (Bjerrum’s area) and correlate with optic disc changes.
- For visual field analysis, automated visual field analyzer that is Humphrey Visual Analyzer is used widely.
- Glaucomatous field defects should always be interpreted in conjunction with clinical features IOP and optic disc changes.
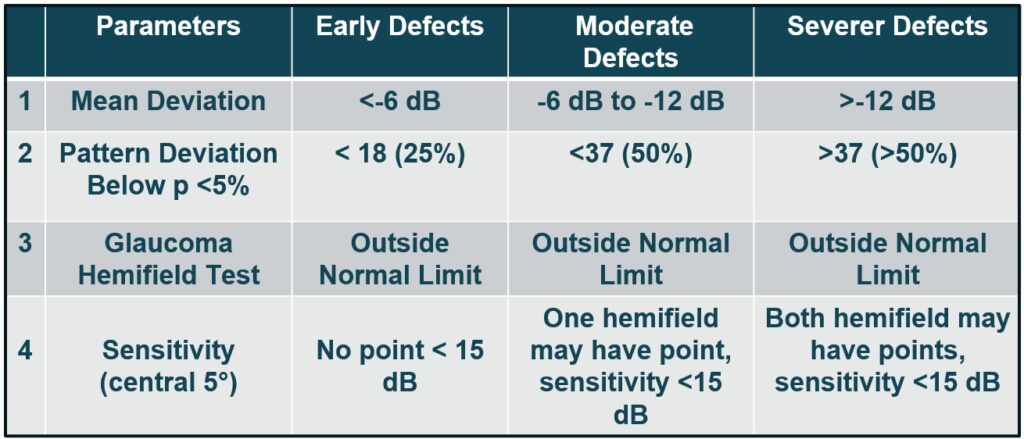
- The criteria to label early, moderate and severe glaucomatous field defect in the HFA central 30-2 test, following point can be analyzed:
Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.





