Clinical Insight:
- In practice it’s found that hyperopic patient can read 6/6 line even with the less power than the power found in retinoscopy.
- Not only hyperopic can read 6/6 line with less power but also mild hyperopic power (up to 1D) is not accepted by the patient.
- Thus, most practitioner end up with Under-correction in hyperopia and no correction in very mild hyperopia (1D).
Why does patient accept under-correction in hyperopia?
- There are two main factors why does hyperopic accept Under-correction in moderate to high hyperopia & don’t accept mild hyperopic correction at all.
- 1. Central Thickness of Plus Lens.
- 2. Stimulation of Accommodation.
1. Central Thickness of Plus Lens
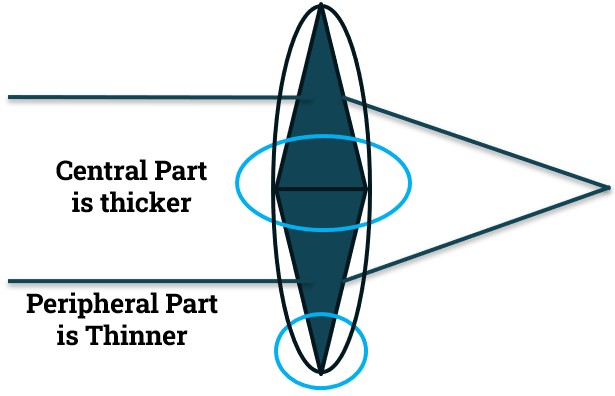
- We know that ophthalmic lenses are made-up of prism.
- Plus lenses are made by placing prism base-to-base direction.
- Rays passing through a prism deviate towards base.
- Thus, plus lenses are converging lens.
- Due to this Base-to-Base position, the central thickness is more than the peripheral in plus lens.
- More the central thickness less the amount of light can pass through the lens.
- Lesser the amount of light can pass through the lens dimmer the objects will be.
- In patient with very mild hyperopia, accommodation helps to read 6/6, when a plus lens is place in front of the patient’s eyes, he/she may say without the plus lens letters are clearer due to decrease in the overall brightness.
- Such patient commonly has a history of headache due to overuse of accommodation and most of the practitioners don’t give plus power as patient is saying that without plus lens Visual Acuity is clearer.
- We can’t depend on patient’s response in such cases, as an optometrist we have to explain that after placing the lens brightness will be less, but letters will be darker & thicker that will relax his/her eye and headache will be gone.
2. Accommodation Stimulation:
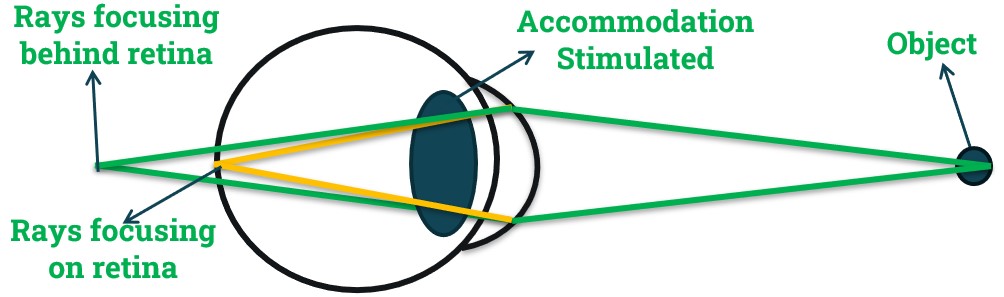
- We know that accommodation helps us to focus on various distances by increasing the converging power of our eyes.
- Accommodation stimulates only when retinal image gets blurred due to rays focus behind (In Hyperopia) the retina.
- If accommodation gets stimulated to the blur due to ray focus in front (In Myopia) of the retina, then image will be more blur.
- Because accommodation increase total power of eyes which will converge the rays further and will lead to more blur retinal image.
- Thus, with help of accommodation hyperopic patient can see distance clearer and called Far Sightedness.
- Myopic can see clearer at near even without stimulating accommodation due to increase total power of eye and called Near Sightedness.
- Let’s see with ray diagrams how does hyperopic accept under-correction during refraction in the next slide.
Mechanism acceptation of Under-correction in Hyperopia:
- Hyperopia is condition where rays from an object at infinity focus behind the retina when accommodation is at rest.
- But accommodation is automatic process, when rays will focus behind the retina, accommodation will be automatically stimulated to bring back the rays on the retina.
- That means when we are doing refraction of a hyperopic patient, accommodation is already activated.
- So, some amount of hyperopia is already corrected by accommodation when we are doing refraction.
- Suppose a patient is having +5.0D of Hyperopia but we may be found +3.0D in refraction and +2.0D may corrected by accommodation.
- So, when we will place a +3.0D lens (under-correction) in trial frame patient will read 6/6 line though the actual power is +5.0D.
- And if we give +3.0D (that is under-correction of 2.0D) as our final refraction, then due overuse of accommodation patient will develop asthenopic symptoms or Accommodative Anomalies.
- As an optometrist we must ensure that accommodation is fully relaxed with the final prescription so that patient don’t develop asthenopic symptoms or accommodative anomalies.
- Now, the question is “How to prevent Under-correction in Hyperopia?”
Prevention of Under-Correction in Hyperopia:
- There are two ways by which we can prevent under-correction in hyperopia during refraction:
- 1. Fogging Method.
- 2. Cycloplegic Refraction.
1. Fogging Method:
- Now as accommodation doesn’t stimulate when rays focus in front of the retina, we can artificially bring the rays in front of retina and then gradually shift the rays on the retina.
- This technique is called Fogging Method in which we place patient refraction or previous glass in the trial frame.
- Then we keep adding plus power in +0.25 steps till visual acuity reduced by 2-3 lines.
- When patient VA is reduced to 2-3 line due to plus power means, patient’s seeing blur due to rays focusing in front of the retina.
- Now we will reduce plus power in +0.25D steps until patient just read 6/6 line for the first time.
- When patient is reading 6/6line for the first time means rays reached on the retina.
- Then leftover power is added to the retinoscopic power to get the final prescription.
- I have already uploaded a video about Complete process of fogging method, I will add the video link in the description.
2. Cycloplegic Refraction.
- Another way to avoid under-correction in hyperopia is Cycloplegic Refraction.
- In this technique we use Cycloplegic Drugs (Drops/Ointments) to paralyze the ciliary muscle.
- When ciliary muscles are paralyzed accommodation can’t activate because when ciliary muscle contract crystalline lens change its shape to more convex and increase total power of our eyes.
- Thus, after paralyzing the ciliary muscle with cycloplegic drugs if we do refraction then we will find the actual power of the patient.
- Suppose in previous patient, in pre-cycloplegic refraction it was found that patient is having +3.0D of hyperopia though he/she was having +5.0D. Now if we apply cycloplegic drops and again do refraction, we will find +5.0D of hyperopia.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.