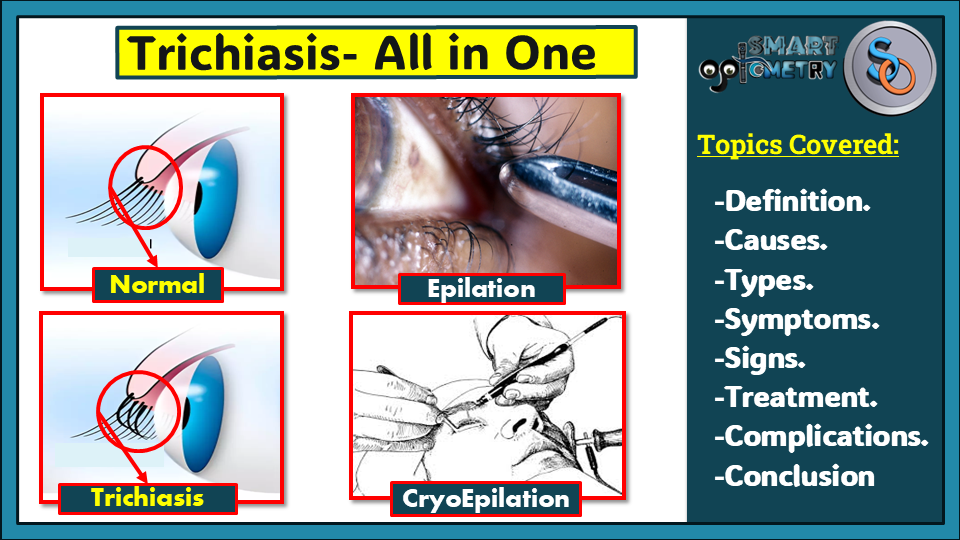
What is Trichiasis?
- Trichiasis refers to inward misdirection of cilia but with normal position of the lid margin.
- In trichiasis position of Eyelid margin will be normal but cilia or eyelashes will be misdirected against the cornea that cause irritation and corneal complications like:
- Recurrent corneal abrasions
- Superficial corneal opacities
- Corneal vascularisation
- Non-healing corneal ulcer
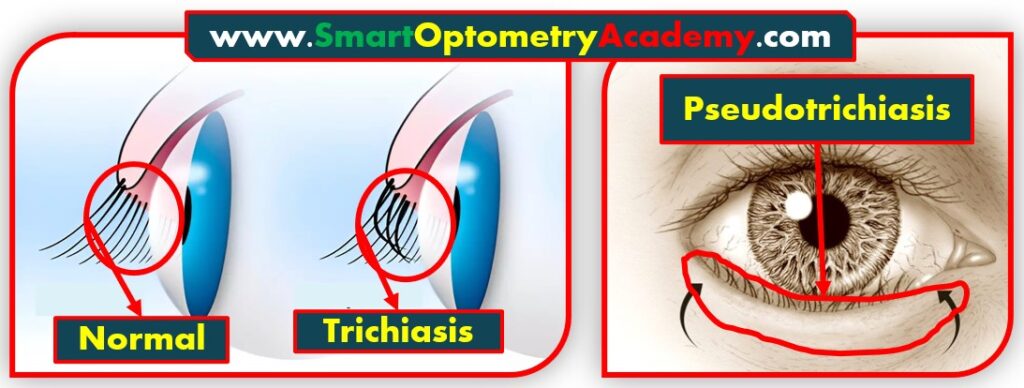
What is Pseudotrichiasis?
- In Pseudotrichiasis, the eyelashes are misdirected towards eyeball due to inward malposition of Eyelid Margin not because of misdirected cilia.
- An Example of Pseudotrichiasis is Entropion, where eyelid margin misdirected inwards and cause inward misdirection of cilia or eyelashes.
.
.
What are the causes of Trichiasis?
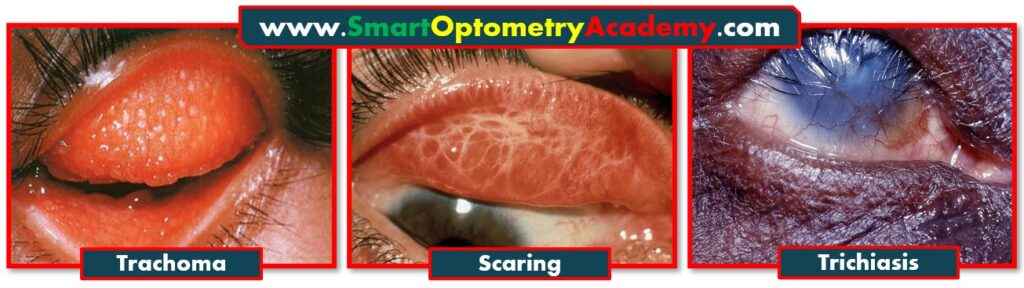
1. Cicatrising Trachoma Leading to trichiasis:
“Cicatrising trachoma is caused by repeated infections with Chlamydia trachomatis. Over time, scarring forms on the conjunctiva and eyelid margin. When scar is healed, it contracts, that pulling the lashes inward toward the cornea, Lead to Trichiasis formation.”
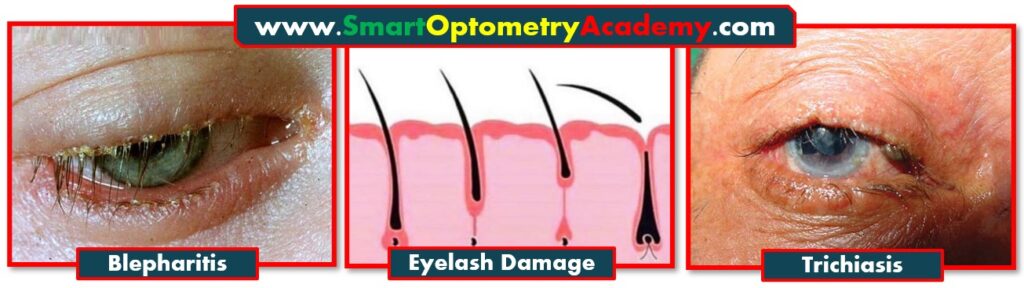
2. Ulcerative Blepharitis Leading to Trichiasis:
“Ulcerative blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins, damages the eyelash follicles. This damage alters the direction of lash growth, leading to trichiasis.”
.
.
3. Healed Membranous Conjunctivitis leading to Trichiasis:
When membranous conjunctivitis healed, scarring forms on the conjunctiva. This scarring contracts the tissue, distorting the lash line and causing inward lash misdirection.”
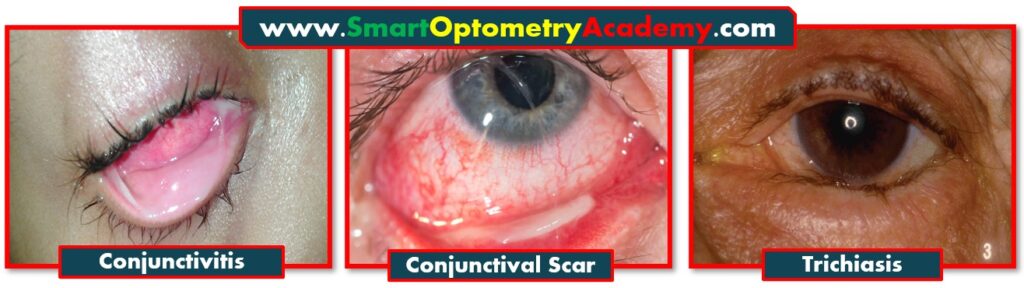
4. External Hordeolum or Stye leading to trichiasis:
“Hordeolum externum or stye, is an infection of the glands near the eyelid margin. When recurrent, it can cause localized scarring, which pulls the lashes inward and lead to trichiasis formation.”
.
.
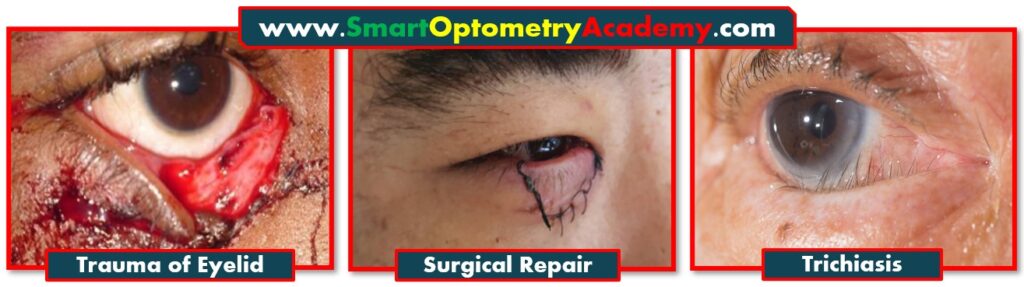
5. Mechanical Injuries leading to trichiasis:
“Mechanical injuries, such as trauma to the eyelid, can disrupt the lash follicles and lid alignment. During healing, the scarring may lead to inward lash growth or trichiasis.”
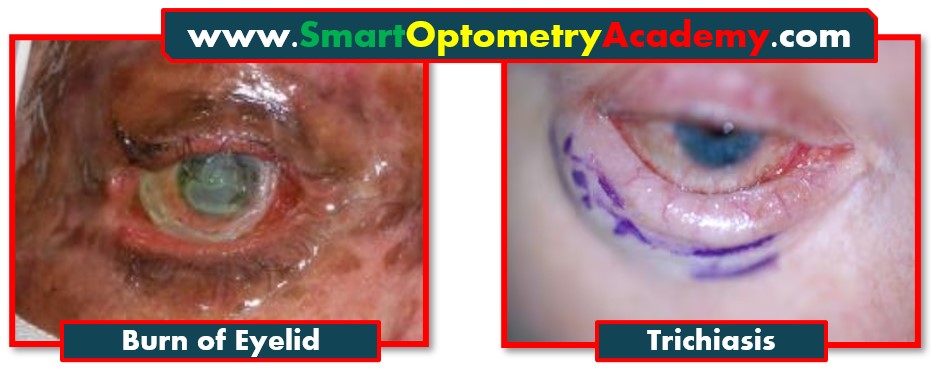
6. Burns leading to trichiasis:
“Burns affecting the eyelids cause scar tissue to form. This scar contracts tissues, distorting the lash line and pushing lashes inward leading to trichiasis formation.”
.
.
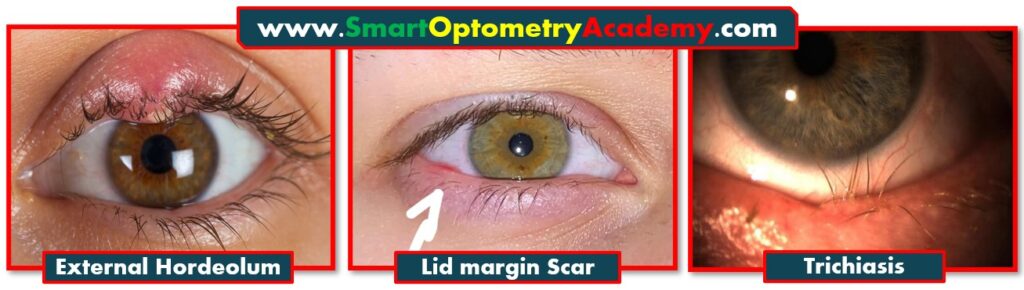
7. Operative Scar on Lid Margin:
“Operative scars from surgeries on the eyelid margin can also distort the natural lash alignment. The scar tissue pulls lashes inward, resulting in trichiasis.”
Clinical Features of Trichiasis:
What are the Symptoms of trichiasis?
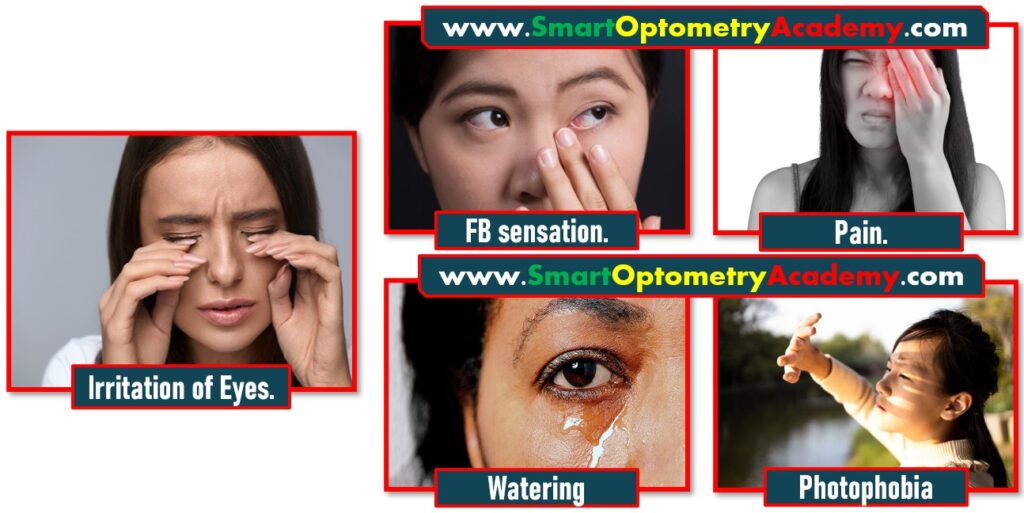
1. Foreign body sensation:
Misdirected eyelashes rub against the cornea and conjunctiva, creating a constant feeling of something being stuck in the eye due to mechanical interaction between the lashes and the sensitive ocular surface.
2. Irritation of Eyes:
The friction caused by inward-facing lashes leads to persistent irritation of the ocular surface, stimulating nerve endings in the cornea and conjunctiva.
3. Pain:
Continuous rubbing of the lashes on the cornea triggers pain sensations. The severity of pain increases with deeper abrasions or chronic inflammation.
4. Excessive Tearing:
Reflex tearing occurs as a protective response by the lacrimal glands to wash away irritants caused by the lashes rubbing against the cornea or conjunctiva.
5. Sensitivity to Light:
Corneal irritation and inflammation make the eye hypersensitive to light, as the affected nerves in the cornea amplify their response to stimuli.
.
.
What are the Signs of Trichiasis?
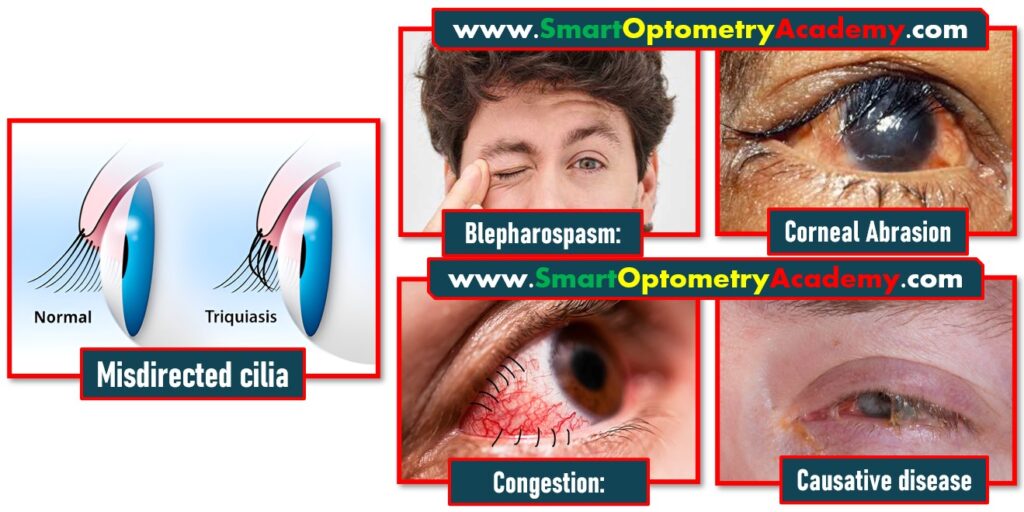
1. Misdirected cilia:
The defining sign of trichiasis is the inward misalignment of eyelashes, which are in direct contact with the ocular surface.
2. Reflex blepharospasm:
Constant irritation and pain stimulate an involuntary closure of the eyelids or blepharospasm, which serves as a protective reflex to shield the eye from further damage.
3. Corneal Abrasion:
When the lashes scratch the corneal epithelium, it leads to abrasions that expose underlying nerve endings, causing light sensitivity and discomfort.
4. Conjunctival congestion:
Persistent friction and irritation result in the dilation of conjunctival blood vessels, causing redness or congestion as part of the inflammatory response.
5. Signs of causative disease:
Trichiasis is often secondary to conditions like trachoma, blepharitis, or trauma. Signs of these conditions may be visible alongside trichiasis.
.
.
What are the Complications Trichiasis?
1. Recurrent corneal abrasions:
The continuous rubbing of misdirected lashes repeatedly damages the corneal epithelium, leading to recurrent abrasions. This impairs healing and makes the cornea vulnerable to infections.
2. Superficial corneal opacities:
Repeated epithelial damage and subsequent healing cause scarring of the corneal stroma, leading to superficial opacities that reduce visual clarity.
3. Corneal vascularization:
Chronic irritation and inflammation stimulate the formation of new blood vessels (neovascularization) in the normally avascular cornea. This response to persistent damage compromises corneal transparency, affecting vision.
4. Non-healing corneal ulcer:
Persistent abrasions, combined with bacterial infections, can lead to ulcers that resist healing due to continuous trauma from misdirected lashes. These ulcers may progress to severe corneal damage, potentially causing permanent vision loss if untreated.
.
.
What is the Treatment of Trichiasis?
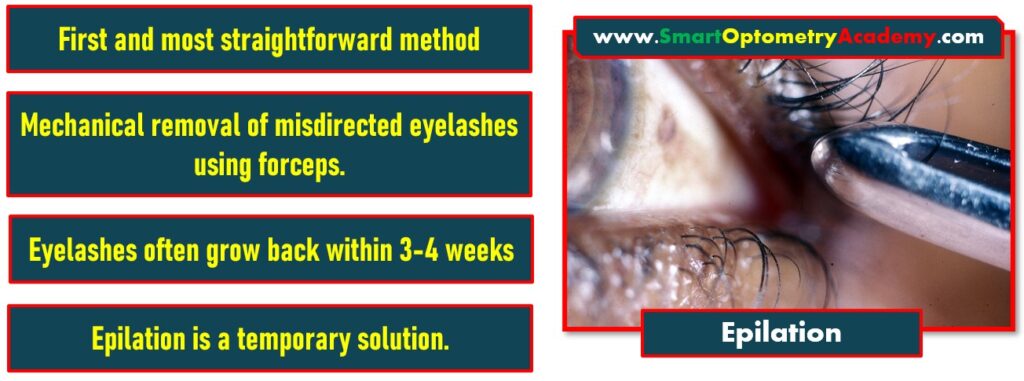
1. Epilation in Trichiasis Management:
- The first and most straightforward method is Epilation.
- This involves the mechanical removal of misdirected eyelashes using forceps.
- While this method is simple, it’s important to note that the eyelashes often grow back within 3-4 weeks, making this a temporary solution.”
.
.
2. Electrolysis Process in Trichiasis Management:
- For a more permanent solution, Electrolysis can be used.
- This procedure destroys the lash follicle using an electric current.
Here’s how it works:
- Local anesthesia is first applied to the eyelid to ensure the procedure is painless.
- A fine needle is inserted into the root of the offending eyelash, and a current of 2 mA is passed through it for 10 seconds.”
- This destroys the lash follicle, and the loosened eyelash is then removed with forceps.”
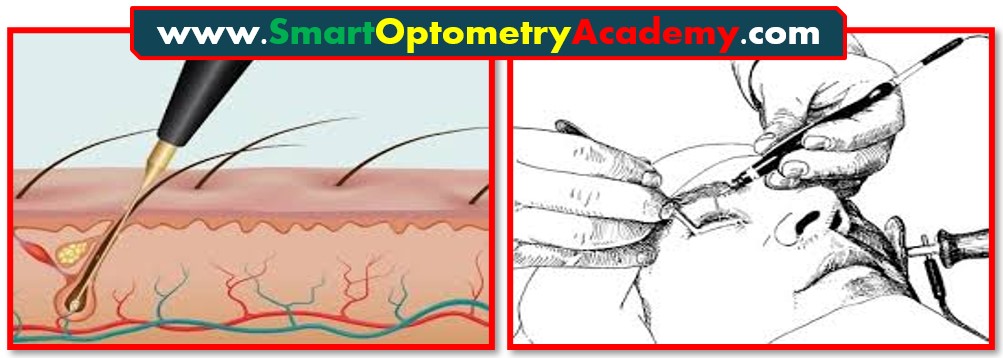
“Electrolysis is effective for treating individual lashes, but it requires precision and may need to be repeated for complete success.”
.
.
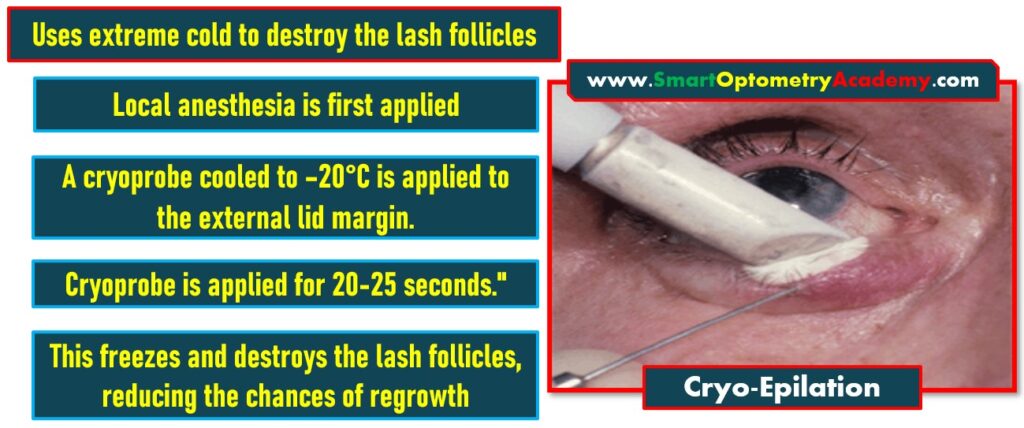
3. Cryo-Epilation in Trichiasis Management:
- Another effective method is Cryo-Epilation. This technique uses extreme cold to destroy the lash follicles.
Here’s how it’s done:
- Local anesthesia is applied to numb the area.
- A cryoprobe cooled to –20°C is applied to the external lid margin for 20-25 seconds.
- This freeze and destroys the lash follicles, reducing the chances of regrowth. However, it’s important to consider the potential downside—cryotherapy can cause depigmentation of the surrounding skin.
.
.
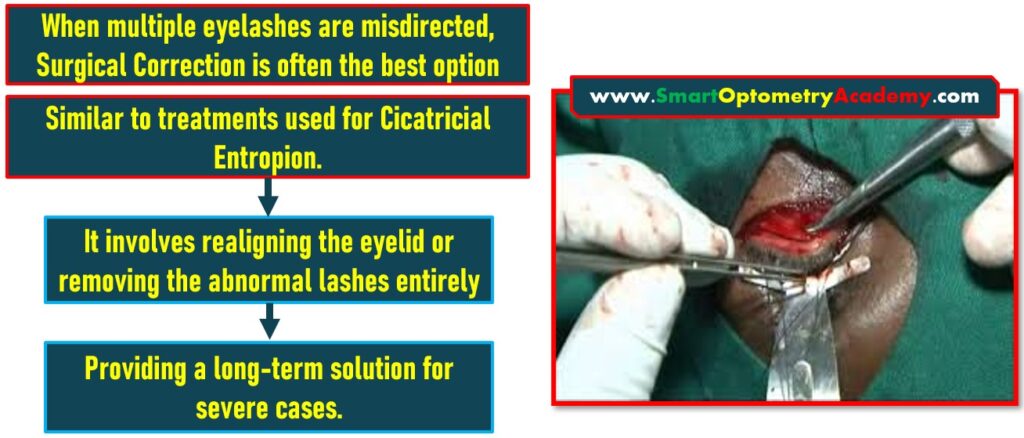
4. Surgical Correction in Trichiasis Management:
- When multiple eyelashes are misdirected, Surgical Correction is often the best option.
- This procedure is similar to treatments used for Cicatricial Entropion.
- It involves realigning the eyelid or removing the abnormal lashes entirely, providing a long-term solution for severe cases.
.
.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.