What is Accommodation Excess?
- When eyes exert more accommodation than required is called Accommodation Excess.
- Accommodative excess is a condition in which the patient has difficulty with all tasks requiring relaxation of accommodation.
- In Accommodation Excess, Accommodative Response is Higher than the Accommodative Stimulus.
- Suppose at 40 cm, Accommodative Stimulus is +2.5D (100/40) but in accommodation excess accommodative response will be more than +2.5D.
- Accommodation Excess is more common in the conditions where rays focus behind the retina like:
- Hyperopia,
- Overcorrected Myopia.
- Under-corrected Hyperopia.
Clinical Features of Accommodation Excess:
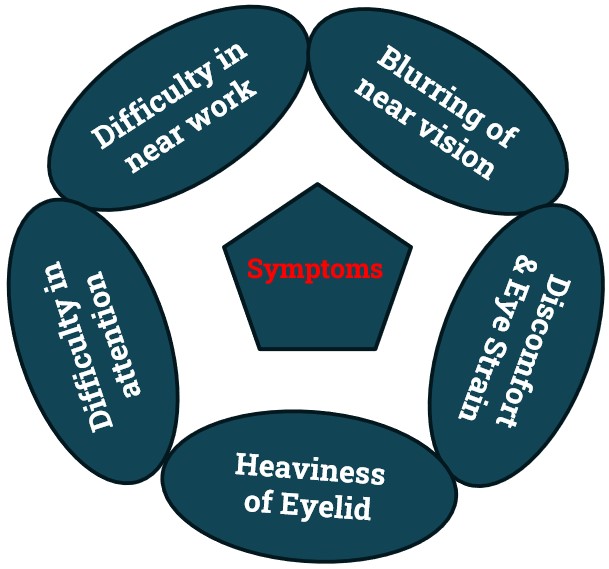
Symptoms of Accommodation Excess:
- Blurred distance vision more prominent after near work.
- Headaches & eyestrain after short periods of reading.
- Difficulty focusing from far to near,
- Sensitivity to light
- These symptoms are more prominent toward the end of the day. Because at beginning of the day we are Energetic and by the time our body becomes tired and can’t exert the extra accommodation.
- The symptom of blurred vision may be associated with both near work and distance tasks, such as looking at the chalkboard, watching television, and driving.
- A characteristic of the blurred vision associated with accommodative excess is that it is often variable and worse toward the end of the day or after extensive near work.
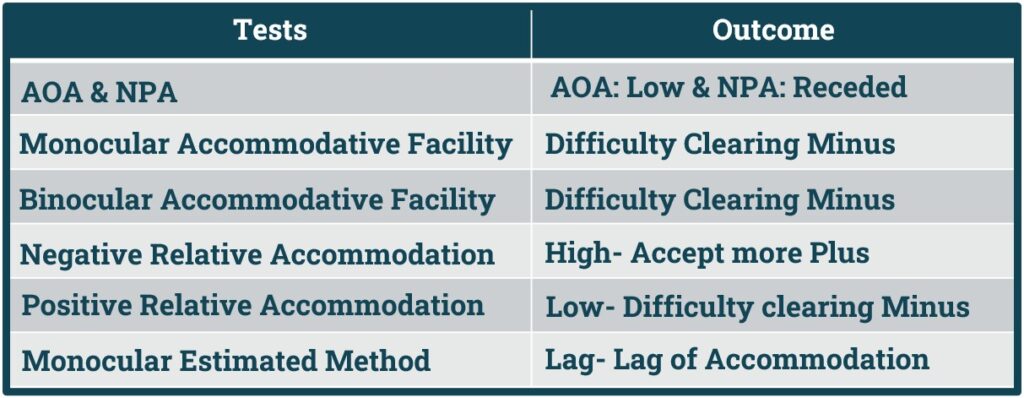
Signs of Accommodation Excess:
- All optometric testing requiring the patient to relax accommodation will be reduced in accommodative excess.
- 1. Amplitude & Near Point of Accommodation:
- Amplitude of accommodation will High and Near Point of Accommodation will be Closer (Nearer).
- 2. Monocular Accommodative Facility:
- Difficulty in Clearing Plus lens.
- 3. Binocular Accommodative Facility:
- Difficulty in Plus Lens.
- 4. Positive Relative Accommodation:
- High- Patient will accept More Minus.
- 5. Negative Relative Accommodation:
- Low- Difficulty in Clearing Plus Lens.
- 6. Monocular Estimated method:
- Low- Lead of Accommodation
Remember: In Accommodation Excess Patient will have difficulty in clearing Plus Lens.
- Both esophoria and exophoria can be present with accommodative excess.
- If the accommodative problem is primary, the patient will overaccommodate relative to the stimulus.
- This leads to excessive accommodative convergence and esophoria at near.
- Another possible scenario is that convergence insufficiency is the primary disorder, and accommodative excess is secondary.
- For example, many convergence insufficiency patients use accommodative convergence to supplement their inadequate positive fusional vergence (PFV).
- Continued use of excessive accommodative convergence may lead to accommodative excess.
Why do Accommodation Excess Patients have difficulty in clearing Plus Lens?
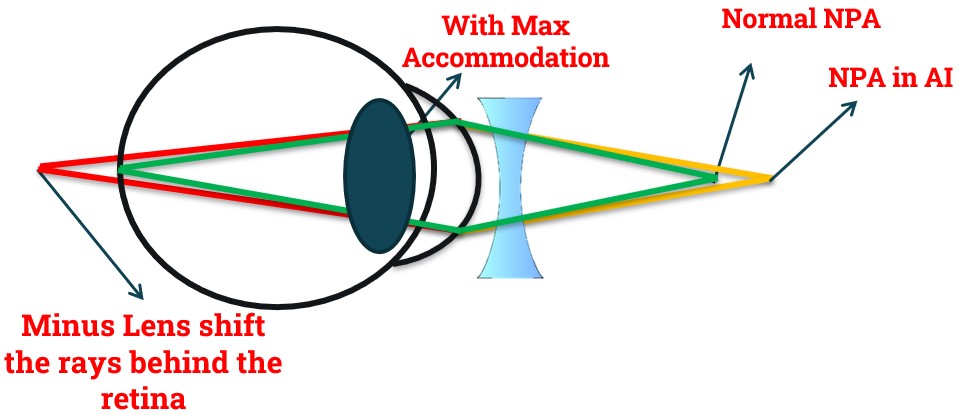
- In Accommodation Excess, Near Point of Accommodation come Closer (Nearer).
- When a +1.50D lens is introduced, it shifts the rays in front of the retina.
- To bring the rays on the retina patient needs to relax 1.5D of accommodation but as patient has accommodation excess it can’t relax the required amount of accommodation and make the image blur.
- Thus, in Accommodative Facility & Negative Relative Accommodation patient with Accommodation Excess face difficulty to Clear Plus Lens.
Management Plan of Accommodation Excess:
- Non-Strabismic Binocular Anomalies Management Plan divided into following Categories:
- 1. Refractive Correction.
- 2. Added Lens Power.
- 3. Prism.
- 4. Occlusion Therapy.
- 5. Vision Therapy.
- 6. Surgery.
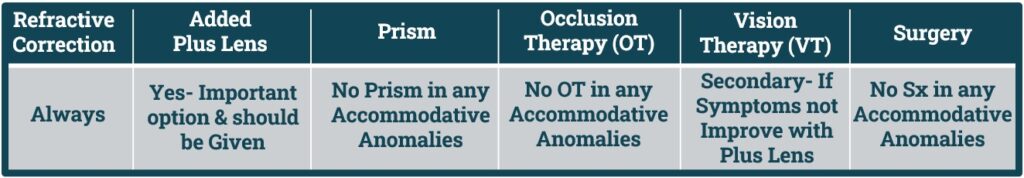
Accommodation Excess Management Include:
- Refractive Correction.
- Vision Therapy.
Let’s See how to give correction in Accommodation Excess.
Refractive Correction in Accommodation Excess:
- Accommodation Excess mostly associated with Hyperopia.
- In Hyperopia, the total converging power of eyes is decrease and rays coming from infinity focus the rays behind the retina.
- When Rays focus behind the retina, accommodation get stimulated and bring back the rays on the retina.
- But as accommodation has to work more than the required to bring the rays on the retina, ultimate it ends up with accommodation excess.
- To correct Hyperopia, we can follow “Maximum Plus for Maximum Vision”.
- But remember in Hyperopia, Eyes accommodate for both for distance and near.
- That means when we are doing refraction of a hyperopic patient, accommodation is already activated.
- So, some amount of hyperopia is already corrected by accommodation when we are doing refraction.
- Suppose a patient is having +5.0D of Hyperopia but we may find +3.0D in refraction and +2.0D may corrected by accommodation.
- So, when we will place a +3.0D lens (under-correction) in trial frame patient will read 6/6 line though the actual power is +5.0D.
- Thus, In Accommodation Excess always better to do Cycloplegic refraction or Fogging for the final prescription.
Quiz for You:
- Q-1: In Accommodation Insufficiency, Positive Relative Accommodation Value will be ……………. .
- A. Normal.
- B. Lower than the Normal.
- C. Higher than the Normal.
- D. None of these.
Type your answer in the Comment
- Q-2: In Accommodation Insufficiency, Monocular Estimated Method will show ……………. .
- A. Normal Accommodation.
- B. Lead of Accommodation.
- C. Lag of Accommodation.
- D. None of these.
Type your answer in the Comment
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.





