What is Accommodation Infacility?
- In Accommodative Infacility patent can’t facilitate accommodation demand for difference accommodative stimulation.
- Patient experiences difficulty changing the accommodative response level; like changing accommodation from near to distance or distance to near.
- Eyes can’t Produce required amount of Accommodative Demand to an accommodative stimulus.
- Generally, to change accommodation response from Near to Far we need 0.56 sec (Average) and to change accommodation response from Far to Near we need 0.64 sec (Average).
- But in Accommodation Infacility it requires more time to response to stimulus then required.
- In Accommodation Infacility Amplitude of Accommodation is normal but patients’ ability to use required Accommodation Quickly and for long periods of time is inadequate.
- So, as an Optometrist if you check only amplitude of accommodation, you may miss the diagnosis of Accommodation Infacility.
- The test that can specifically diagnose Accommodation Infacility are:
- Negative Relative Accommodation.
- Positive Relative Accommodation.
- Monocular Accommodative Facility.
- Binocular Accommodative Facility.
Clinical Features of Accommodation Infacility:

Symptoms of Accommodation Infacility
- Most symptoms are associated with reading or other close work.
- Common complaints are:
- Difficulty changing focus from one distance to another,
- Blurred vision,
- Headaches,
- Eyestrain,
- Difficulty sustaining and attending to reading and other close work,
- Fatigue
The most characteristic symptom of accommodative infacility is difficulty changing focus from one distance to another.
Signs of Accommodation Infacility:
- 1. Amplitude & Near Point of Accommodation:
- Amplitude of accommodation will be Normal and Near Point of Accommodation will be Normal.
- 2. Monocular Accommodative Facility:
- Less Cycle- Difficulty in Clearing both Plus/Minus lens.
- 3. Binocular Accommodative Facility:
- Less Cycle- Difficulty in Clearing both Plus/Minus lens.
Note: The diagnosis of Accommodation Infacility is confirmed just because of less number of cycle in accommodation facility test rather less number of cycle due to difficulty in clearing both Plus and Minus Lens.
- 4. Negative Relative Accommodation:
- Low- Difficulty in Clearing Plus Lens.
- 5. Positive Relative Accommodation:
- Low- Difficulty in Clearing Minus Lens.
- 6. Monocular Estimated method:
- Normal = +0.25 to +0.75D
Remember: Tests that are required to relax & stimulation of accommodation will be reduced in Accommodation Infacility. Like: Accommodative Facility, Relative Accommodation.
Note: Esophoria at near is the most common binocular vision problem associated with accommodative infacility, although exophoria and even intermittent exotropia have been reported.
Why does AI have difficulty in clearing Minus Lens?
Accommodative Facility:
- Diagnosis does not finalize with less number of cycle rather if less number of cycle due to difficulty in clearing both plus & minus lens. Like low number of cycle in monocular and binocular facility may be due to clearing in plus lens but normal with minus lens or difficulty with minus lens but normal with plus lens.
- Esophoria at near is the most common binocular vision problem associated with accommodative infacility, although exophoria and even intermittent exotropia have been reported.
Management Plan of Accommodation Infacility:
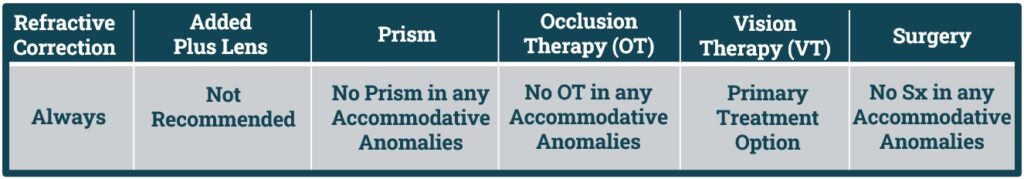
- Non-Strabismic Binocular Anomalies Management Plan divided into following Categories:
- 1. Refractive Correction.
- 2. Added Lens Power.
- 3. Prism.
- 4. Occlusion Therapy.
- 5. Vision Therapy.
- 6. Surgery.
- For Accommodation Infacility the Primary treatment option is:
- 1. Refractive Correction.
- 2. Vision Therapy.
1. Refractive Correction in Accommodation Infacility:
- The first management consideration for accommodation infacility is correction of ametropia.
- When dealing with patients with accommodative infacility, even small degrees of refractive correction may be significant.
- Prescribing for small degrees of hyperopia, astigmatism, and small differences in refractive error between the two eyes may provide some immediate relief of symptoms for the patient.
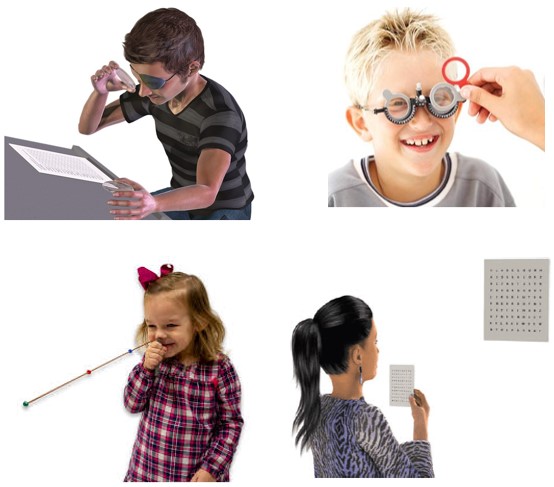

2. Vision Therapies for Accommodation Infacility:
- Though computer-based exercises have higher outcome, due to their expensiveness it is not possible to perform.
- Simple Manual exercises are:
- Lens Sorting.
- Loose Lens Rock.
- Brock String.
- Hart Chart.
- Accommodative Flipper.
- Bug in the String.
- Barrel card Exercises.
- The purpose of these exercises is to improve the accommodative Response.
- I will cover each of these exercises in Separate Blog.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.





2 Comments
Here is Accommodation Insufficiency Blog: https://smartoptometryacademy.com/accommodation-insufficiency/
Excellent Post. Please make post on Accommodation Insufficiency