What is Accommodation Insufficiency?
- When Amplitude of Accommodation is below the lower limit of the expected value for the patient’s age.
- Suppose at the age 18 years, patients minimum amplitude of accommodation according to Hoffsterer’s formula is:
- AOA = 15 – (0.25 X Age)
- AOA = 15 – (0.25 X 18) or
- AOA = 15 – 4.5
- AOA = 10.50D.
- If a 18years old patient has AOA of less than 10.5D than it may be a case of Accommodation Insufficiency.
- Generally, at least 2D less than minimum AOA for the age is considered Accommodation Insufficiency.
Clinical Features of Accommodation Insufficiency:
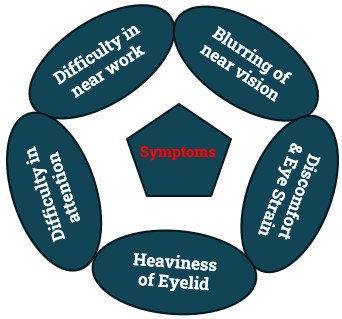
Symptoms of Accommodation Insufficiency:
- The most common complaints include:
- Difficulty in near work but comfortable at distance.
- Gradually Blurring of near vision.
- Discomfort and Eye Strain associated with near tasks.
- Heaviness of Eyelid associated with near tasks.
- Difficulty with attention and concentration while reading.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Patients may also complain of an inability to concentrate, a loss of comprehension over time, and words moving on the page.
- All of these symptoms are associated with reading or other close work.
Signs of Accommodation Insufficiency:
- Accommodative insufficiency is a disorder in which the patient experiences difficulty with any optometric testing that requires stimulation of accommodation.
- Any test that involves the use of minus lenses will generally yield a reduced finding.
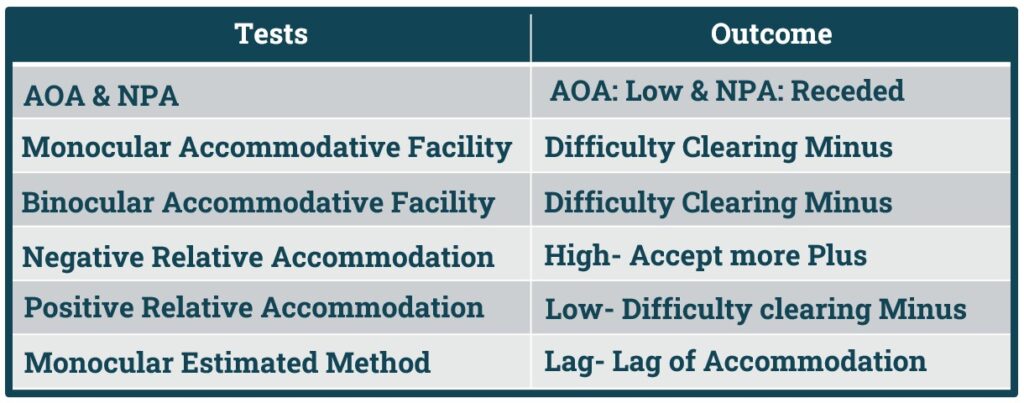
- Amplitude & Near Point of Accommodation:
- Amplitude of accommodation will be low and Near Point of Accommodation will be Receded (Farer).
- Monocular Accommodative Facility:
- Difficulty in Clearing Minus lens.
- Binocular Accommodative Facility:
- Difficulty in Minus Lens.
- Negative Relative Accommodation:
- High- Patient will accept More Plus.
- Positive Relative Accommodation:
- Low- Difficulty in Clearing Minus Lens.
- Monocular Estimated method:
- Lag- Lag of Accommodation
Remember: In Accommodation the Patient will have difficulty in clearing Minus Lens.
- Accommodative insufficiency may also be associated with a binocular vision problem.
- It is not unusual to find a small degree of esophoria in cases of accommodative insufficiency.
- A likely explanation is that the patient uses additional innervation to try to overcome the accommodative problem, which stimulates accommodative convergence, causing an esophoria.
Why Minus Lens Difficulty in Accommodation Insufficiency?
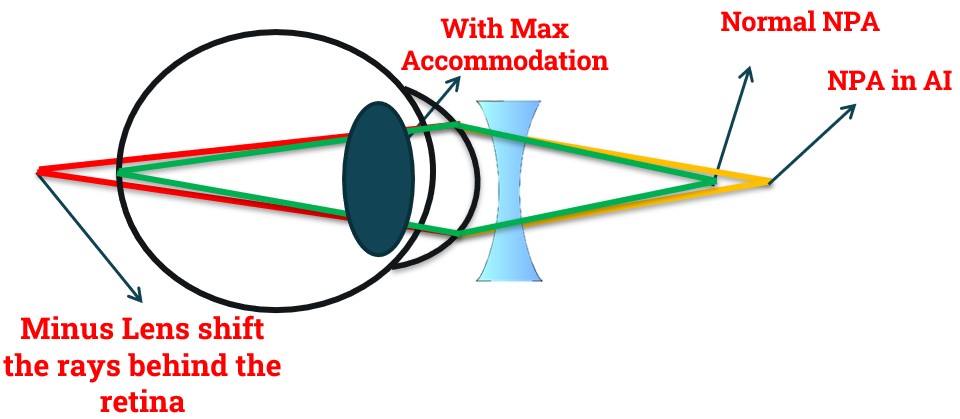
- In Accommodation Insufficiency Near Point of Accommodation Receded (Farer).
- When a -1.50D lens is introduced, it shifts the rays behind the retina.
- To bring the rays on the retina patient needs 1.5D of accommodation but patient already has insufficient accommodation.
- So, introducing a Minus lens in Accommodative Insufficiency may blur the image.
- Thus, in Accommodative Facility & Positive Relative Accommodation patient with Accommodation Insufficiency face difficulty to Clear Minus Lens.
Pseudo-Convergence Insufficiency in Accommodation Insufficiency:
- A condition known as Pseudo-convergence Insufficiency has also been related to accommodative insufficiency.
- In Accommodation Insufficiency, the patient has difficulty accommodating and therefore underaccommodates relative to the stimulus. As a result, less accommodative convergence is available, the measured exophoria is larger, and a greater demand is placed on positive fusional convergence.
- Typically, such patients will also have a receded near point of convergence because of the reduced amplitude of accommodation and the lack of accommodative convergence.
Management of Accommodation Insufficiency:
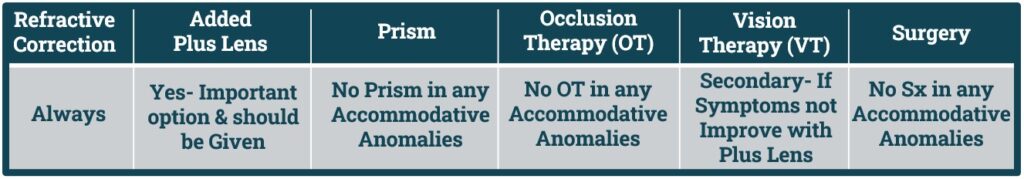
- Non-Strabismic Binocular Anomalies Management Plan divided into following Categories:
- 1. Refractive Correction.
- 2. Added Lens Power.
- 3. Prism.
- 4. Occlusion Therapy.
- 5. Vision Therapy.
- 6. Surgery.
Management of Accommodation Insufficiency include following:
- 1. Refractive Correction.
- 2. Added Plus Lens.
- 3. Vision Therapy.
Let’s See how to give correction in Accommodation insufficiency and how to detect added Plus lens power.
Refractive Correction in Accommodation Insufficiency:
- Accommodation Insufficiency mostly associated with myopia.
- Due increase total converging power of our eyes, patient can see clear even without using Accommodation.
- Thus, in uncorrected Myopia or under-corrected myopia patient develop Accommodation Insufficiency.
- To correct the myopia, we can give full correction or follow Minimum minus maximum vision.
- But when we correct Myopia suddenly eyes need Accommodation to work more to focus rays on the retina.
- As Accommodation is insufficient, accommodation can’t fulfil the new demand of accommodation and patient face difficulty with near tasks with Myopic Correction.
- Thus, giving a plus lens in Accommodation Insufficiency is an important option.
- But remember, this plus lens is temporary to relied on the symptoms.
- With time we need to remove the plus lens when accommodation back to normal limit.
Let’s see how to identify the amount of Plus lens we need to prescribe in Accommodation Insufficiency in the Next Slide.
Added Plus lens Power in Accommodation Insufficiency:
- The Added Plus lens power may be determined by different methods:
- 1. Based on PRA and NRA values.
- 2. MEM retinoscopy.
- 3. Based on AC/A ratio.
- Here We will discuss about How to find Added Plus Power Based on PRA & NRA Values.
- A simple formula can be used to identify added plus power:
- Plus Power Needed = NRA – PRA/2
(Numerical Difference of NRA & PRA is taken, No plus or minus sign is taken)
Example: Suppose NRA is +3.50D and PRA -1.50D.
- So Added Plus lens will be: 3.5 – 1.50/2 or 2/2 or 1D.
- So, initially with distance myopic correction we will start with a plus lens of 1D.
- Then with time when accommodation will be normal, we must remove the plus power.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.





