Q-1: Main source of glucose for corneal layer is from (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) plasma
(B) blood
(C) aqueous humour
(D) tear film
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: c. aqueous humour
The cornea is an avascular structure, meaning it does not have its own blood supply. Therefore, it relies on the aqueous humour, the clear fluid filling the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye, for its glucose and nutrient needs. This fluid provides the necessary nourishment to keep the corneal cells healthy and functioning.
Struggling with your optometry government job preparation? Let Samir Sir, the founder of Smart Optometry, guide you to success. Enroll in our “Gov Job Preparation” course, and we’ll provide the roadmap. Your dream job at GSSSB, AIIMS, RRB, or DHS is within reach!
.
.
Q-2: At birth, the eye has the following, EXCEPT : (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Underdeveloped macula
(B) Hypermetropia
(C) Small pupil
(D) Deep anterior chamber
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: d. Deep anterior chamber
The eye of a newborn is anatomically different from that of an adult. While it has an underdeveloped macula, hypermetropia, and a small pupil, the anterior chamber is typically shallow, not deep. The anterior chamber deepens as the eye grows and matures.
.
.
Q-3: During the act of accommodation the zonules (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) becomes tense
(B) Slackens
(C) relaxes
(D) Both B & C
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: (D) Both B & C
Accommodation is the process by which the eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. During this process, the ciliary muscles contract, which releases tension on the zonules. As the zonules slacken zonules relaxes and the natural elasticity of the lens causes it to become more convex, thus increasing its refractive power.
Unlock your potential with our “Gov Job Preparation” course. Gain access to a massive library of 5000+ subject-wise MCQs, 1000+ previous year questions, detailed notes, and video lectures. Everything you need for exams like GSSSB, PSC, and DMER is in one place.
.
.
Q-4: Which of the following is carcinogenic (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Autoclave
(B) Ethylene oxide
(C) Hot air oven
(D) None of the above
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: b. Ethylene oxide
Ethylene oxide is a gas used for sterilization in medical and pharmaceutical fields. However, it is also a known human carcinogen and a mutagen. It is classified as a hazardous substance due to its toxic effects on living organisms.
.
.
Q-5: Colour sense is a function of (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) cones
(B) rods
(C) retinal pigment epithelium
(D) ganglion cells
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: a. cones
Cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina that are responsible for color vision and visual acuity. They are most concentrated in the fovea, the central part of the macula, where vision is sharpest. Rods, on the other hand, are responsible for vision in low light conditions.
Prepare for a full year of opportunities! Our “Gov Job Preparation” course gives you 12 months of access to top-quality materials and support. Cover all major exams like GSSSB, AIIMS, RRB, Ophthalmic Officer without buying multiple courses. It’s the smartest investment for your career.
.
.
Q-6: The bony orbit is made up of: (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) 5 bones
(B) 7 bones
(C) 8 bones
(D) 9 bones
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: b. 7 bones
The bony orbit is a socket in the skull that holds the eyeball. It is composed of seven bones: frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, sphenoid, ethmoid, lacrimal, and palatine. These bones protect the eye from injury and provide a stable structure for the muscles that control eye movement.
.
.
Q-7: Average diameter of optic disc is (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) 1.5 mm
(B) 2.0 mm
(C) 2.5 mm
(D) 5.0 mm
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: a. 1.5 mm
The optic disc is the circular area where the optic nerve enters the retina. It is a critical anatomical landmark in ophthalmology. Its average diameter is approximately 1.5 mm, which is important for diagnosing conditions like papilledema or optic nerve atrophy.
Don’t study alone! Our “Gov Job Preparation” course includes group chat and live support to clear all your doubts instantly. With guidance from Samir Sir and a community of fellow aspirants, you’ll stay motivated and on track.
.
.
Q-8: Each of the following is a type of dry heat sterilization, EXCEPT: (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Flaming
(B) Autoclave
(C) Incineration
(D) Hot air oven
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: b. Autoclave
Dry heat sterilization methods use high temperatures without moisture to kill microorganisms. Flaming, incineration, and hot air ovens are all examples of this. An autoclave, however, uses moist heat (steam under pressure) for sterilization.
.
.
Q-9: Optic Nerve is backward continuation of (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Ganglion cell layer
(B) Nerve fiber layer
(C) Inner plexiform layer
(D) Outer nuclear layer
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: b. Nerve fiber layer
The optic nerve is formed by the axons of the retinal ganglion cells. These axons course along the surface of the retina, forming the nerve fiber layer. They then converge at the optic disc to exit the eye and form the optic nerve.
.
Ready to secure your government job in optometry? The “Gov Job Preparation” course is your final destination. With a proven success strategy, expert mentorship, and over 6000 MCQs, we make your preparation seamless and effective. Click the link to begin your journey!
.
Q-10: Glands of Krause and Wolfring are: (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Modified sweat glands
(B) Modified sebaceous glands
(C) Accessory lacrimal glands
(D) Main lacrimal glands
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: c. Accessory lacrimal glands
The glands of Krause and Wolfring are small accessory lacrimal glands found in the conjunctiva. They are responsible for a small portion of the basal tear secretion, which helps to maintain the lubrication and health of the ocular surface.
.
.
Q-11: The far point at which smallest object can be seen clearly is called (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Punctum proximum
(B) Punctum remotum
(C) Range of accommodation
(D) Amplitude of accommodation
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: b. Punctum remotum
The punctum remotum is the farthest point from the eye at which an object can be seen clearly. For an emmetropic (normal) eye, the punctum remotum is at infinity. For a myopic eye, it is at a finite distance, and for a hyperopic eye, it is a virtual point behind the eye.
Struggling with your optometry government job preparation? Let Samir Sir, the founder of Smart Optometry, guide you to success. Enroll in our “Gov Job Preparation” course, and we’ll provide the roadmap. Your dream job at GSSSB, AIIMS, RRB, or DHS is within reach!
.
.
Q-12: Fumigation is done by : (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Formalin gas
(B) Chlorine gas
(C) Methylene oxide
(D) All of the above
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: a. Formalin gas
Fumigation is the process of disinfecting an area using a chemical fumigant. Formalin gas, which is a gaseous form of formaldehyde, is commonly used for this purpose, particularly for sterilizing operating rooms and hospital wards.
.
.
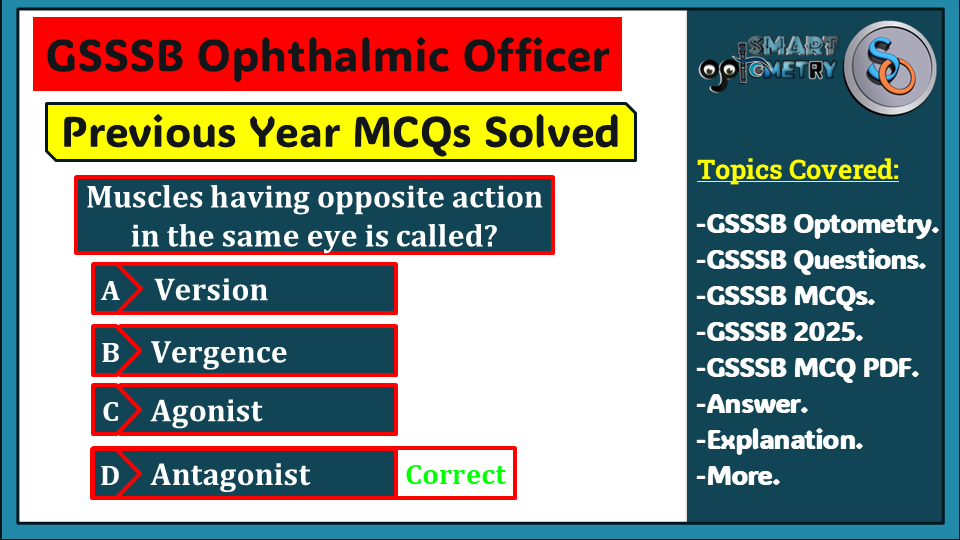
Q-13: Muscles having opposite action in the same eye is called (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Version
(B) Vergence
(C) Agonist
(D) Antagonist
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: d. Antagonist
In the context of eye muscles, an antagonist is a muscle that opposes the action of another muscle, known as the agonist. For example, in a vertical eye movement, the superior rectus and inferior rectus muscles are antagonists.
Unlock your potential with our “Gov Job Preparation” course. Gain access to a massive library of 5000+ subject-wise MCQs, 1000+ previous year questions, detailed notes, and video lectures. Everything you need for exams like GSSSB, PSC, and DMER is in one place.
.
.
Q-14: The physiological tone of the ciliary muscle is : (GSSSB Optometry Previous Year MCQs)
(A) 1.0 dioptre
(B) 1.5 dioptres
(C) 2.0 dioptres
(D) 2.5 dioptres
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: a. 1.0 dioptre
The ciliary muscle, even in its relaxed state, maintains a certain level of contraction known as its physiological tone. This tone contributes a small amount of accommodation, typically around 1.0 dioptre, which is why an eye is often considered to be focused at a point slightly closer than infinity when fully relaxed.
.
.
Q-15: Which system measures the PD using “corneal reflex” ? (GSSSB Ophthalmic Officer Previous Year MCQs)
(A) Topcon PD-2, PD meter
(B) Essilor Pupilometer
(C) PD Ruler
(D) Both A and B
Click “Show more” to see the answer and explanation.
Answer: d. Both A and B
Both the Topcon PD-2 PD meter and the Essilor Pupilometer are types of pupillometers that use the corneal reflex to measure a patient’s pupillary distance (PD). These devices are more accurate than a standard PD ruler because they rely on the reflection of a light source on the cornea, which provides a more precise measurement.
Prepare for a full year of opportunities! Our “Gov Job Preparation” course gives you 12 months of access to top-quality materials and support. Cover all major exams like GSSSB, AIIMS, RRB, Ophthalmic Officer without buying multiple courses. It’s the smartest investment for your career.
.
.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.
.
.