You will be to know about: Definition, example, principle, procedure, interpretation, normal scan, color code, RNFL assessment and indication of Optical Coherence Tomography.
Table of Contents
Introduction of Optical Coherence Tomography:
- OCT is an optical instrument that can perform cross-sectional image of biological tissue within less than 10-micron axial resolution using light waves.
- Retina is easily accessible to the external light; hence it is especially suited for retinal disorders.
- The information provided by OCT is similar to in vivo histopathology of the retina.
Example:
- Zeiss stratus OCT
- Topcon 3D OCT-1000
Basic principle of Optical Coherence Tomography:
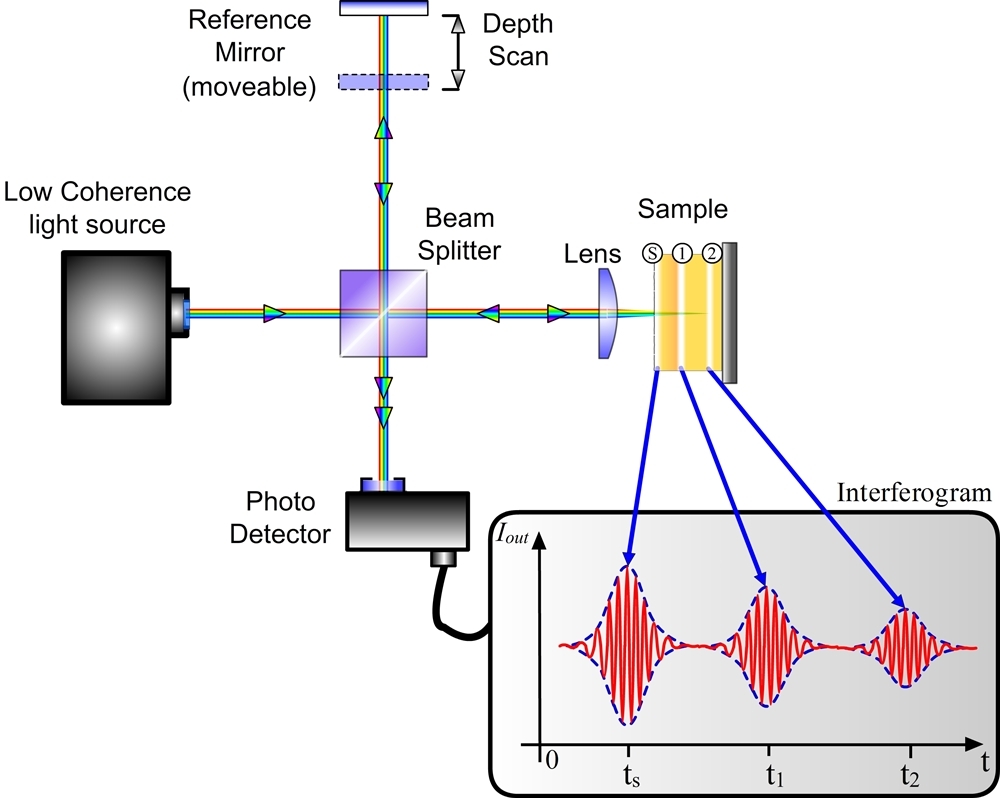
- It is a imaging technology projected light beam (820nm) near infrared light
- The beam is then split into two beams (Probe beam & Reference beam) by Beam splitter.
- Probe beam reach to the target tissue (retina) & reference beam reach to the reference mirror at a known distance.
- The echo time delay of light reflected various layers of target tissue (retina) is compared with the echo time delay of light reflected from the reference mirror.
- A positive interference is produced when light reflected from target tissue & reference mirror arrives simultaneously.
- This interference is measured by a photodetector which finally produces a range of time delays for comparison.
- The interferometer integrates several data points over 2mm depth to construct a tomogram of retinal structures.
- It is a real time tomogram using false color scale & different colors represent light backscattering from the different layers of retina.
Procedure of Optical Coherence Tomography:
- STEP-1:
- Activation of instrument & entering patients’ data
- Step-2: Patients preparation:
- Pupil dilate with mydriatics (tropicamide) Asked to look into the internal fixation target light in the ocular lens.
- Step-3: Protocol for scan acquisition:
- Selected as per the case requirements.
- The scanning beam is placed on the target area and scans are obtained.
- Step-4: Production & display image:
- Several data points are integrated by the interferometer to construct a tomogram of the target area.
- The tomogram is displayed in either grey scale or false color on a high-resolution computer screen.
Normal oct scan of retina:
- The normal OCT scan of the retina allows cross-sectional study of the macula, peripapillary region including RNFL and ONH region.
Color coding of oct scan:
- RED-YELLOW COLORS: represents areas of maximal optical reflection & backscattering.
- BLUE & BLACK: Represents areas of minimal optical reflection & backscattering.
Indication of Optical Coherence Tomography:
A. RETINAL DISEASE:
1. PRE & POST MACULAR HOLE SURGERY:
- Helps to determine presence & grade of macular hole.
- To determine whether anatomical closure has occurred or not.
2. MACULAR EDEMA:
- Detection & monitoring edema during treatment
3. SUB-RETINAL NEOVASCULAR MEMBRANE:
- To evaluate pre & post treatment features
B. GLAUCOMA:
- OCT scan patterns for the optic nerve head and peripapillary retinal fiber layer
- Glaucoma follow-up to detect evidence of progression.
Watch our Youtube Lecture on OCT: https://youtu.be/jbuIfHmAwz4?si=VCMDPReZWr-7N2mG
Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.