Retinoscopy vs Retinoscope
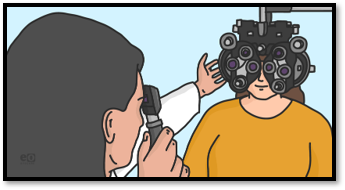
What is Retinoscopy:
- Retinoscopy is a clinical procedure by which refractive error of eyes are identified objectively with the Retinoscope.
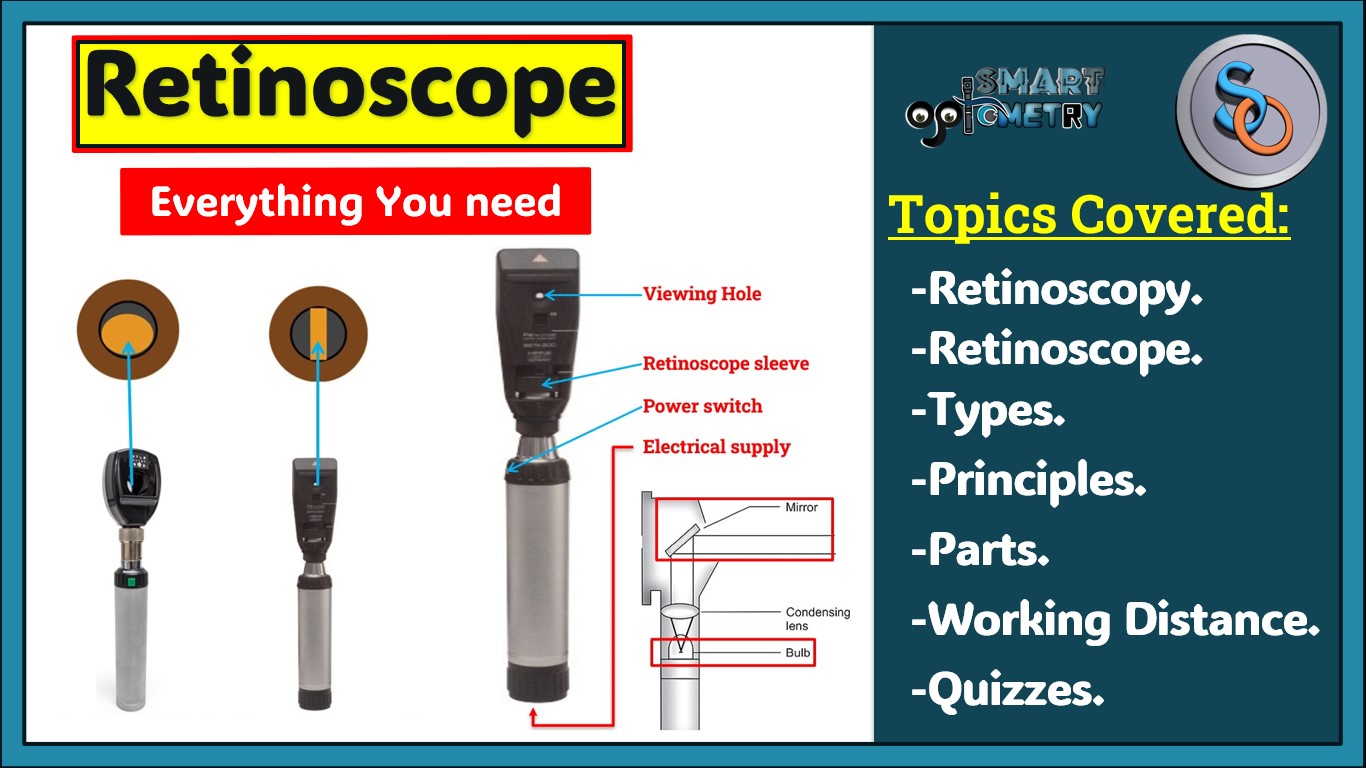
Retinoscope:
- Retinoscope is an optical instrument used to estimate the refractive error of the eyes objectively.
- Retinoscopy helps us to identify not only refractive error but also other ocular conditions. Like:
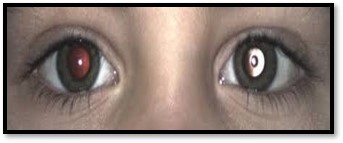
a. Media Opacities:
- Corneal Opacity,
- Vitreal Opacity,
- Posterior Capsular Opacity (PCO)
b. Cataract:
- Posterior Subcapsular Cataract (PSC)
c. Retinal Detachment (Rare):
- Greyish Reflex.
Principle of Retinoscope:
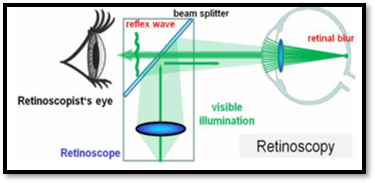
What is the Principle of Retinoscope?
- Based on “Focault’s Principle”
- When light reflected from a mirror into the eye, the direction in which the light will travel across the pupillary area will depend upon the refractive state of the eye:
With movement:
- Hypermetropia or Myopia less than Working Distance Power,
Against Movement:
- Myopia.
Neutral:
- Myopia (Equal to working Distance Power)
Same movement in both Meridian:
- Emmetropia or Spherical Refractive Error.
Different Movement in Both Meridian:
- Astigmatism.
Types of Retinoscope:
What are the types of Retinoscope?
1. Reflecting (mirror) retinoscopes:
- Reflecting (mirror) retinoscopes are cheap and at one time were the most commonly employed.
- However, presently these are rarely used.
- A source of light is required when using mirror retinoscope, which is kept above and behind the head of the patient.
2. Self-illuminated retinoscopes:
- Self-illuminated retinoscopes are costly but handy.
- These have become more popular nowadays.
- Two types of self-illuminated retinoscope available are:
- A spot retinoscope.
- A streak retinoscope.
- The streak retinoscope is more popular, and most commonly used, as it is more sensitive than spot retinoscope in detecting astigmatism
Spot vs Streak Retinoscopy:
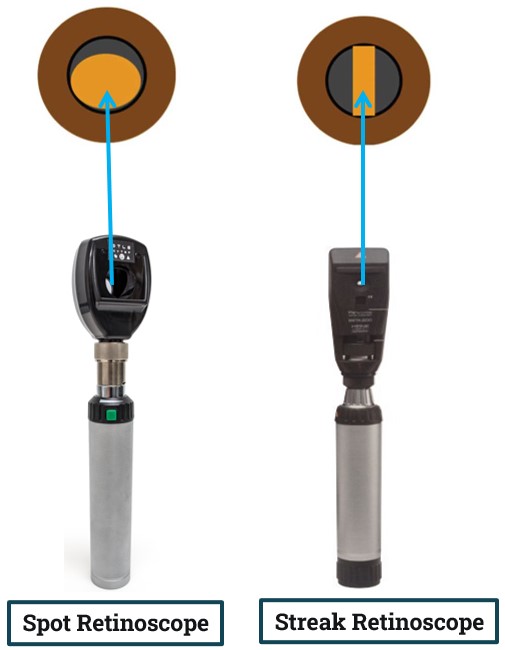

A. Spot self-illuminous retinoscope:
- It provides a round shape illumination thus it’s called “Spot Retinoscope”
- It consists of a bulb with a tiny, wired filament about 1-2 mm in size.
- This is imaged by a convex lens of about 20 mm focal length to give a beam of light which is reflected by a mirror at 45°.
B. Streak Retinoscope:
- In streak retinoscope the illumination is provided by a special bulb that has a straight filament, thus forming a ‘streak’ in its projection.
Note: In clinical Practice we mostly use Streak Retinoscope. So we will cover details about Streak Retinoscope here.
Parts of Streak Retinoscope:
What are the parts of a Streak Retinoscope?
Power switch:
- To turn the retinoscope on and off.
- To control the brightness of the light.
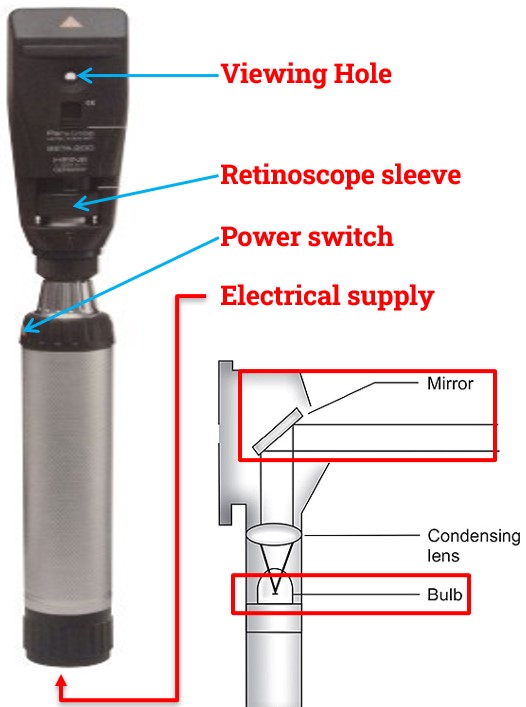

Small globe (light bulb):
- It provides the light.
Electrical supply:
- Batteries (disposable or rechargeable) in the retinoscope handle.
- A power cord to connect the retinoscope to the main electricity.
Mirror:
- It reflects light from the globe into the person’s eye.
Retinoscope aperture (viewing hole):
- It allows the ret reflex to be seen.
Retinoscope sleeve:
- It rotates the axis of the retinoscope’s light and changes the light beam from divergent to convergent light.
Characteristics of Ret Reflex of Streak Retinoscope:
What are the Characteristics of Ret Reflex Seen through Streak Retinoscope:
1. Brightness:
- Gets brighter as we get closer to the neutral point.
2. Direction of movement:
a. With movement:
- Hypermetropia or myopia less than working distance power,
b. Against movement:
- Myopia more than working distance power.
c. Neutral:
- Myopia (equal to working distance power)
3. Speed:
- Becomes faster at closer to neutralization.

4. Thickness:
- Becomes wider when getting closer to neutralization.
Working Distance & Working Distance Power:
What is Working Distance in Retinoscopy?
- Distance from which retinoscopy is performed or the distance between the spectacle plane to retinoscopy.
What is Working Distance Power in Retinoscopy?
- Power used to subtract the working distance is called Working Distance Power.
Why do we need to subtract the working distance:
- We do retinoscopy to identify the power of the patient at the spectacle plane.
- But the position of a retinoscopy is away from spectacle plane that is normally 67 CM away from spectacle plane.
- That means we identify the power of that patient at 67 CM not in the spectacle plane due to which we got 1.5D more power during retinoscopy.
- So, to identify the power that is required in spectacle plane we need to subtract the distance from retinoscopic value.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.