Table of Contents
What is a Slit Lamp?
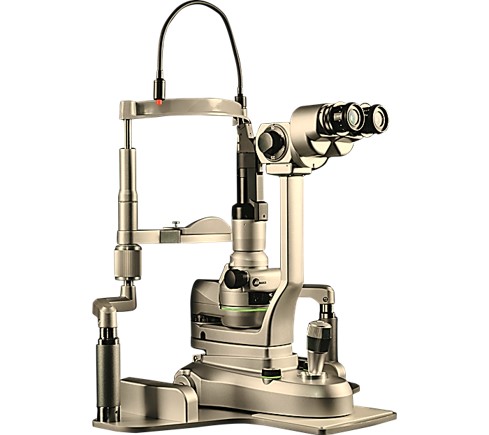

The slit-lamp biomicroscope is an optical instrument that emits a narrow, slit-like, but intense beam of light, used to examine the interior structures of the eye from the cornea to the anterior part of the vitreous.
Invention:
The slit-lamp was invented by Gullstrand in 1921.
Capabilities:
Modern slit-lamps, equipped with various accessory devices, not only provide magnified views of the eye’s structures from the cornea to the retina but also enable photography for documentation and quantitative measurements.
Measurements:
The slit lamp can measure intraocular pressure, endothelial cell counts, pupil size, corneal thickness, and anterior chamber depth.
Magnification Range:
Most slit-lamps offer magnification ranging from 6X to 40X, allowing detailed examination of ocular structures.
Principle of Slit Lamp:
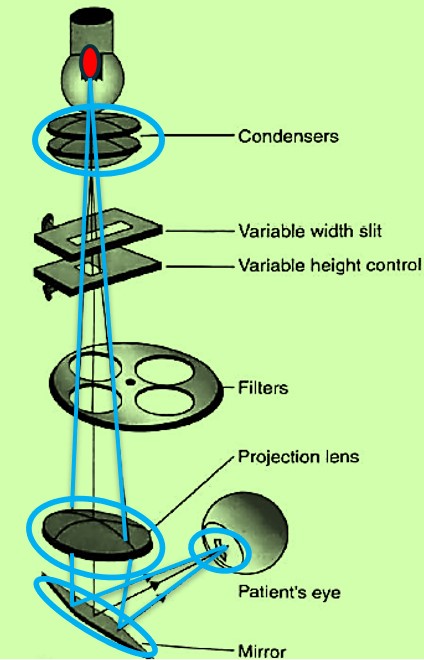
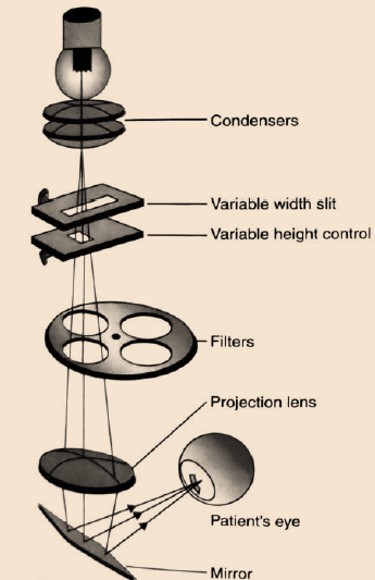
- The slit-lamp biomicroscope operates on the principle of producing a narrow, intense beam of light, which the examiner observes under magnification.
- Central to its function is the Koeller illumination system, which enhances the quality and precision of the illumination.
- In this system, the filament of the light source is focused by condenser lenses at or near the projection lens.
- This projection lens then projects the image of the slit into the patient’s eye, illuminating the specific area being examined.
- This setup allows for detailed and magnified visualization of the eye’s internal structures, from the cornea to the anterior part of the vitreous, facilitating precise examination and diagnosis.
Observable Parts by a Slit Lamp:
- Eyelids & Lashes.
- Tear Film.
- Conjunctiva.
- Limbus.
- Cornea.
- Aqueous Humor.
- Anterior Chamber.
- Iris & Pupil.
- Crystalline Lens.
- Anterior Vitreous.
Types of Slit Lamp:
There are two main types of slit-lamp biomicroscopes:
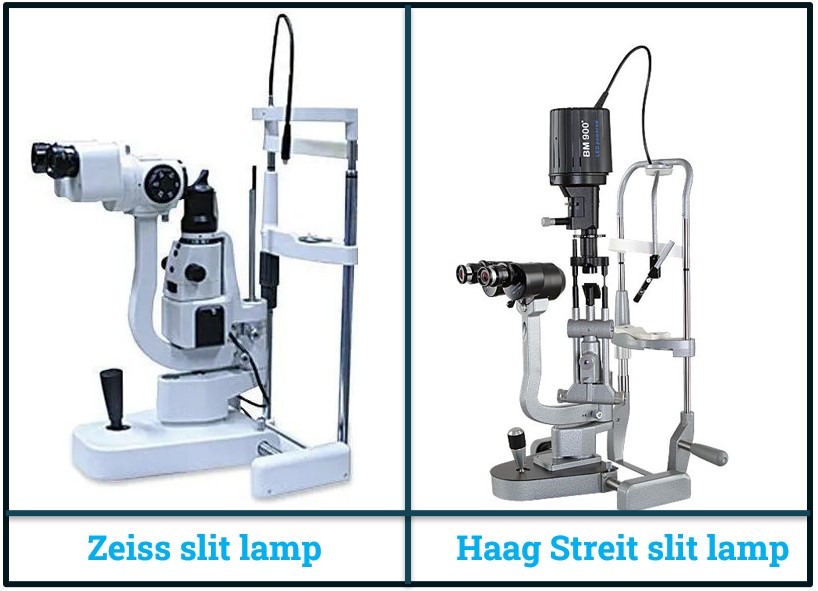

1. Zeiss Slit Lamp Biomicroscope:
- In the Zeiss type, the light source is positioned at the base of the instrument.
2. Haag Streit Slit Lamp Biomicroscope:
- In the Haag Streit type, the light source is located at the top of the instrument.
- These two types differ primarily in the placement of the light source, which affects the design and possibly the ergonomics and user preference.
Parts of Slit Lamp:
- A slit-lamp is composed of three parts:
- A. Observation system (microscope).
- B. Illumination system.
- C. Mechanical support system.
A. Observation System of Slit Lamp Biomicroscope:
The observation system of a slit lamp biomicroscope consists of several key components designed to provide detailed and accurate visualization of the eye:
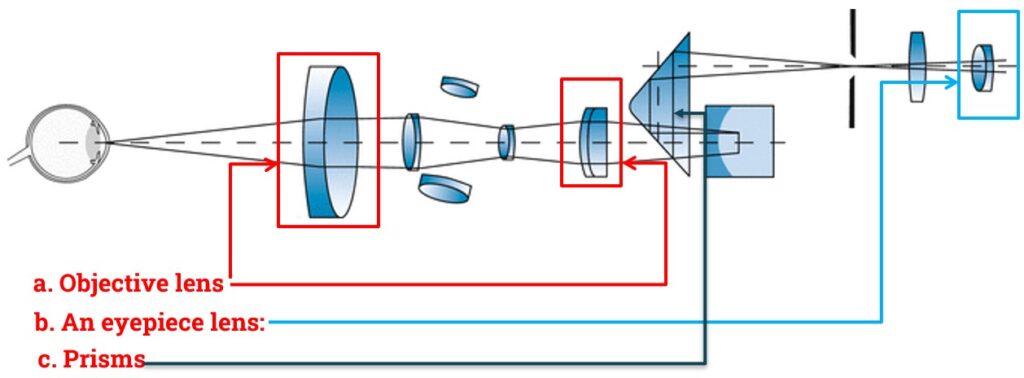
1. Objective Lens:
- The objective lens consists of two plano-convex lenses.
- Together, these lenses provide a composite power of +22 diopters (D).
2. Eyepiece Lens:
- The eyepiece has a lens with a power of +10 diopters (D).
- It offers good stereopsis, enhancing depth perception.
- The eyepiece tubes are angled to converge at 10-15° for comfortable binocular viewing.
3. Prisms:
- The image formed by the slit lamp is initially inverted.
- A pair of prisms is used in the observation system to reinvert the image, ensuring the observer sees a correctly oriented view.
B. Illumination System of Slit Lamp Biomicroscope
- The illumination system of a slit lamp biomicroscope is composed of several components that work together to provide precise and adjustable lighting for eye examinations:
1. Light Source:
- Historically, various light sources were used, including Nernst lamps, Nitra lamps, arc lamps, and mercury vapor lamps.
- Modern slit lamps typically use halogen lamps, which provide illumination levels ranging from 200,000 to 400,000 lux.
2. Condenser Lens System:
- This system includes a couple of plano-convex lenses with their convex surfaces facing each other, focusing the light for optimal illumination.
3. Slit and Other Diaphragms:
- The height and width of the slit can be adjusted using dedicated knobs, allowing for precise control over the light beam’s shape and size.
4. Filters:
- Different filters can be inserted into the illumination beam to enhance specific observations.
- Commonly provided filters include cobalt blue and red-free filters.
5. Projection Lens:
- This lens forms an image of the slit at the eye, with a typically small diameter to focus the light precisely on the area of interest.
6. Reflecting Mirror or Prism:
- A mirror or prism is used to reflect the light along a horizontal axis, directing the illumination precisely where it is needed in the eye.
C. Mechanical System of Slit Lamp Biomicroscope
The mechanical system of a slit lamp biomicroscope includes several key components that allow for precise and adjustable positioning of the instrument and patient support:
i. Joystick Arrangement:
- The joystick enables the movement of the microscope and illumination system towards or away from the eye, and from side to side, facilitating precise adjustments during the examination.
ii. Up and Down Movement Arrangement:
- The up and down movement of the entire illumination and viewing system is controlled by a screw device, allowing the system to be adjusted relative to the chin rest.
iii. Patient Support Arrangement:
- The slit lamp includes a vertically movable chin rest and an adjustable table height to accommodate patients of various sizes, ensuring comfort and proper alignment.
iv. Fixation Target:
A movable fixation target is provided to aid in keeping the patient’s eye steady and focused during the examination, improving the accuracy and ease of the procedure.
- Check Our Courses: Ophthalmic Instrumentation, Clinical Refraction, Contact Lens, Binocular Vision, Dispensing Optics, MCQs in Optometry
- Download our App “Optometry Notes & MCQs” from Google Play Store.






5 Comments
Thank you for your appreciation.
awesome
Stay with smart optometry and study optometry smartly..
Thanks so much! ✨
Stay with us for more precise notes. Don’t forget to invite yours friends…….